SEO is not what it used to be.
After numerous algorithm updates and the introduction of RankBrain as a ranking factor, Google is changing the way it answers our questions.
Today, improving your Google ranking is less about keywords and more about content.
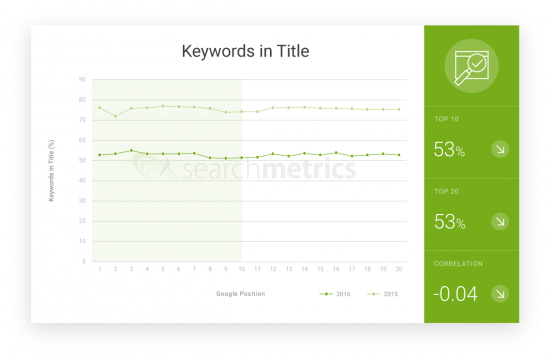
In a 2016 study by SearchMetrics, keyword targeting wasn’t the main indicator of ranking success; the study found that only 53% of the top 20 search queries prominently featured the target keyword.
What’s more is that less than 40% of those results contained the keyword in – long to be thought one of the primary SEO locations – the H1 tag.
Let’s think about that for a second.
Let’s say we do a search for internet marketing:
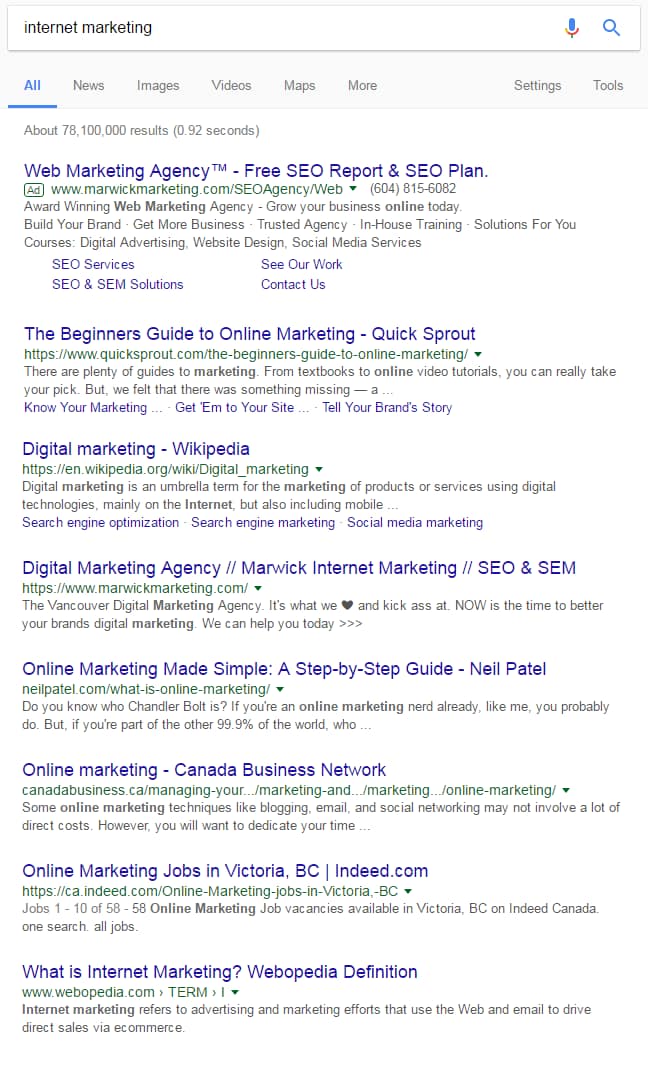
How many times do we see the term internet marketing in the page title?
Very few times, indeed.
I bet if we were to click on each of these results, we’d find that only about half – if that – have internet marketing in their H1 tag.
Whereas before, including the keyword in the page title and using it in the H1 tag were considered essential to winning a top spot in the search results, this is no longer the case!
So what does Google care about?
The answer to that question lies in Google’s mission statement:

Note the last two adjectives: accessible and useful.
Those two words are the key to ranking better in 2017.
Google wants to provide the best search results.
Period.
And they’ve gotten better at doing this by recognizing that keywords aren’t everything.
Instead, providing useful, accessible content that is relevant to what the searcher is after is the ultimate goal.
If we create useful content that is accessible to people and relevant to what the searcher is looking for, we will be rewarded in the search results.
But what makes for useful and accessible content and where do we start in improving our ranking in 2017?
In this post, I’m going to walk you through 5 simple things you can do to improve your rankings in 2017.
Table of Contents
By implementing these into your web strategy you’ll be well on your way to higher rankings in Google.
Let’s get started.
1. Speed Up Your Site
It wasn’t long ago that Google announced that they would be using the speed of your website as a ranking factor in their algorithm.
And this, of course, makes sense as a fast-loading website improves overall user experience.
Think about it:
Have you ever been frustrated by a web page that took too long to load?
I know I have, and if you’re anything like me, you probably abandoned the web page pretty quickly.
This is what happens when your web page isn’t optimized for speed and performance.
Additionally, studies have been done that show that a slow-loading web page leads to less time spent on your site, higher bounce rates, and fewer conversions.
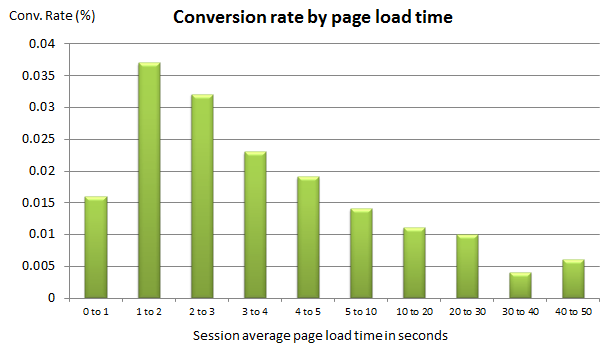
All this to say: a slow-loading diminishes accessibility.
In fact, your website can be penalized if it is too slow.
If you want to rank better in 2017, you need to consider the speed and performance of your website.
To get a sense of where your website stands currently, here are a few tools to test the speed and performance of your site:
I recommend plugging your website into all three to get the clearest picture of your website’s performance.
From there, you will better understand what you need to do to speed up your site.
While sources speculate that page speed isn’t a direct ranking factor, one thing is known for sure: faster websites make for happier visitors and better-ranked websites.
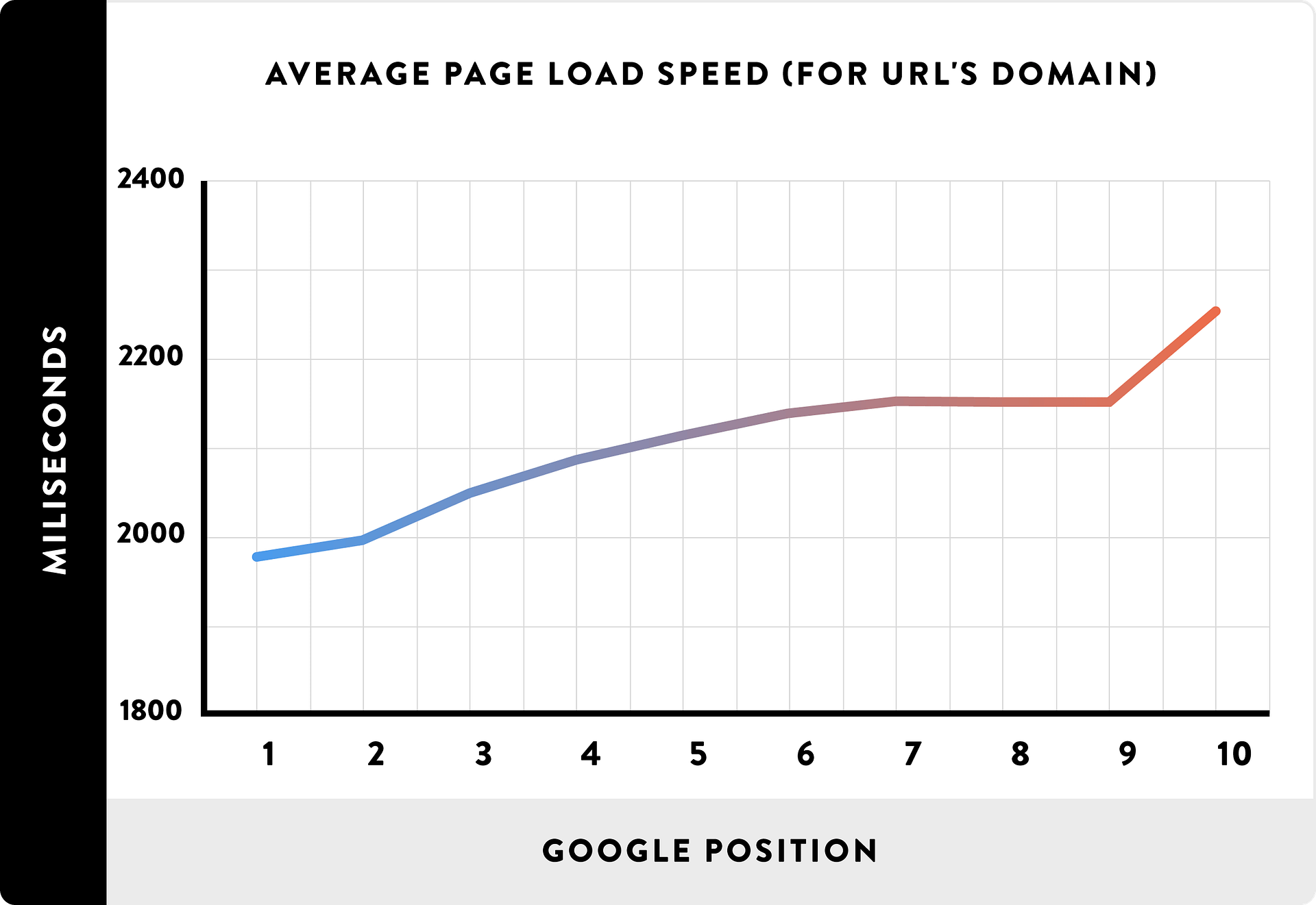
If you’re serious about improving your ranking on Google in 2017, you simply can’t ignore the speed and accessibility of your website!
2. Optimize for Mobile
It’s a mobile world with at least half of web traffic today coming from mobile devices.
In fact, Google suggests that that number is even higher and continues to increase each year.

What’s more is that the way people use search on mobile is different than how they use a desktop website.
For example, people are more inclined to take action within an hour after making a search on their smartphones.

If that’s not enough motivation to make sure your website is mobile-optimized, consider this:
In the last 18 months, Google has changed the way it indexes web pages, moving from a desktop-first approach to a mobile-first approach.
What this means is that Google first considers how your website performs on mobile devices before ranking your site. If your website performs poorly, you can expect to see that reflected in your search ranking.
How to optimize your website for mobile?
As a web developer and SEO, I can tell you that if you don’t currently have a mobile-friendly website, there isn’t really a quick-fix for obtaining one – or at least obtaining one worth having!
What’s typically required is to take a mobile-first approach.
That is to consider how your website is experienced first on a mobile device including how content is presented within the design then expanding it out to larger screens and desktop devices.
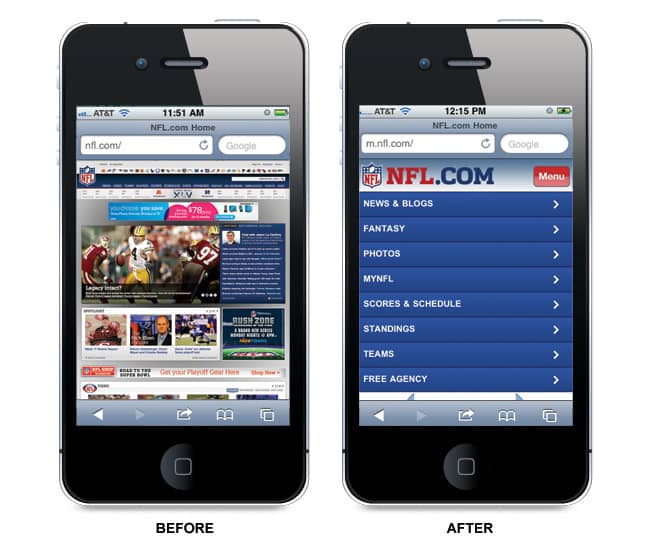
A mobile-optimized website is designed to be easily accessible from a smartphone or tablet.
Things like making links finger-clickable and avoiding using bandwidth-intensive design elements like images in your mobile website all contribute to the mobile-friendliness of your website.
Is Your Website Mobile-Friendly?
To quickly find out if your website is mobile-friendly, use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
This free tool will tell you how mobile-friendly your page is and give you suggestions on things to fix if it isn’t optimized for mobile.
Developer Tip: To test how your web page would look across various screen sizes, grab your browser window and resize it! A mobile-friendly website will adapt well to varying screen sizes while a website that isn’t will remain fixed at one size.
If you do have a website that is mobile-friendly here are some resources you can check out to learn more about further optimizing your website for mobile:
Not only do mobile-optimized websites lead to better rankings on Google, they make your content accessible in a very mobile world.
You simply can’t afford not to have a mobile-friendly website!
3. Write Longer Content
Since Google’s Panda algorithm in 2011, the pages that rank better in search also tend to be more informational, comprehensive, and in-depth.
This contradicts what used to do well in search: perfunctory articles of around 500 words that were secondary to the web pages real purpose, which was to sell you something you probably didn’t need or want.
Ultimately, the latter web pages didn’t provide much use or benefit to search users, so Google decidedly dropped them from their top search results.
Instead, what garners high rankings nowadays is useful content, content that robustly and comprehensively answers a question or fulfills a need.
The best-ranking web pages are also highly relevant to the searcher’s intent.
Perform any search in the pursuit to learn more about a subject and you are bound to find well-written articles with at least 1,000 words that dutifully answer your questions.
More and more, longer articles are appearing higher in the search rankings.
In a recent study by Capsicum Mediaworks, researchers found that the average content length of the top 10 results was around 1,900 words:
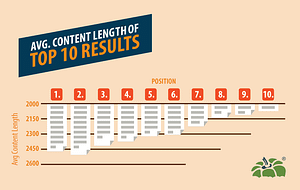
Not too surprisingly, this longer, richer content tends to get shared more often, too.
Buzzsumo analyzed 100 million articles and concluded that longer-form content gets the most shares online:
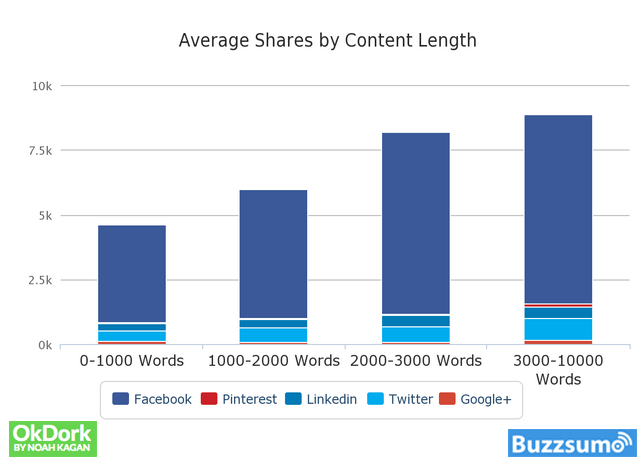
Neil Patel of Quicksprout also did a test using over 300 hundred of his blog posts and found that posts with over 1,500 hundred words received more social shares on Twitter and Facebook:
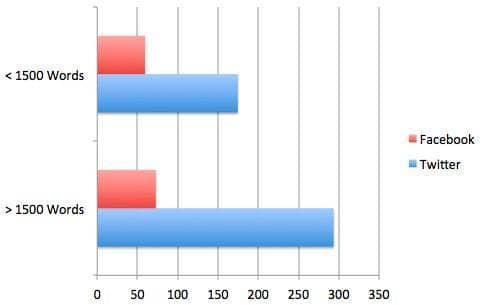
The sharing of content has very positive SEO return-on-investment, too, creating more interest and potential for new links to your site.
Backlinks (links from other websites and third-parties that point to your site) are a powerful ranking factor in Google and other search engines.
Essentially, they serve as a vote of confidence in favor of your website.
Consider this:
If some third-party is willingly linking to your website it sends a clear message to Google that other people find your content useful, valuable and trust it enough to link their website to it.
The more of these outside parties that are linking to your website, the more trust you build among search engines and the better you rank in the search results.
For a quality and in-depth look at what it takes to build backlinks yourself, check out this step-by-step article on how to build high-quality backlinks.
Keeping in line with our look at longer content, the people at Moz wanted to see if there was any correlation between longer content and more backlinks. This is what they found:
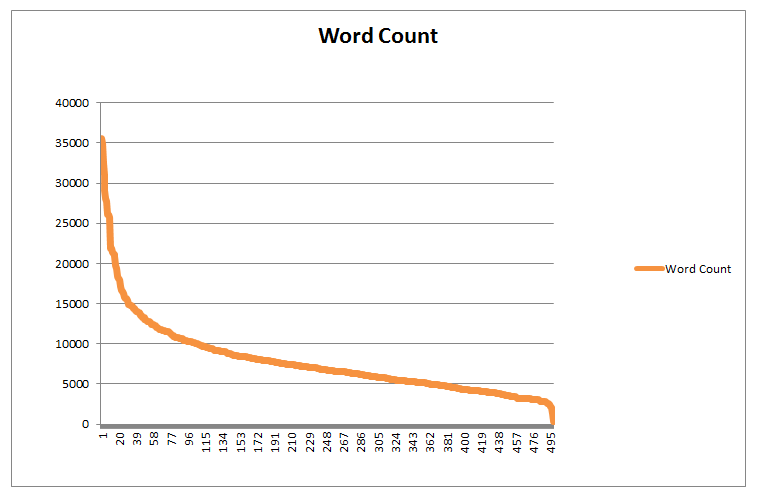
Now compared with the number of backlinks:
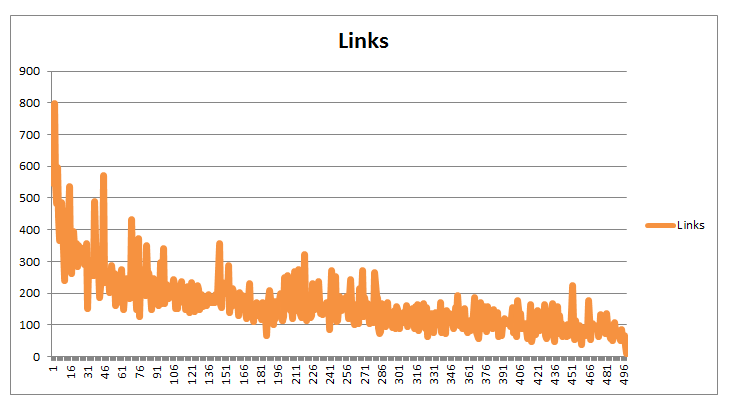
As you can see, pages with the greater amount of words tended to earn more backlinks than pages with a lower word count.
Now, this doesn’t mean you can just fill your page with fluff and expect to gain backlinks and social shares.
People – and Google – are smart enough to recognize fluff from useful content.
So be sure to put in the time and effort to create real, useful content the helps people out.
If the prospect of earning more backlinks and social shares isn’t enough to encourage you to write longer content, here a few more SEO benefits that you can gain from writing long-form content:
- Increased User Engagement – Longer content increases time on page, a User Engagement metric that is likely factored into overall search rankings.
- Attract More Relevant Visitors – Through writing longer, more in-depth articles, you more effectively tell Google what your page is about. This increases the likelihood that your content will be returned for long-tail keyword search, highly specific search phrases that lead to more relevant, targeted visitors.
- Increased Conversions – Studies show that longer-form content does a better job of converting customers than content that is shorter and less comprehensive.
How to write more in-depth, relevant content
Writing relevant content starts with first understanding who you’re writing for and then researching keywords in order to determine what people are actually typing into the search query box.
Once you understand who your audience is and what they’re typing into Google, you can then begin to create relevant content around your audience’s intent.
Here is a guide to get you started: 11 Tips for Writing Better Long-Form Content
If you want to dig more into the topic of why long content wins out over shorter content plus how create longer pieces of content for yourself, check out:
At the end of the day, longer content offers users and search engines more information to sink their teeth into.
In the process, you’ll be helping your SEO by sending more positive user signals to Google; you’ll also be providing more value to your customers which can lead to more conversions and more leads for your business.
4. Up Your Click-Through Rate
Another lesser-known SEO strategy to ranking better in 2017 is improving your Click-Through Rate.
What is Click-Through Rate?
Click-Through Rate, or CTR for short, is the number of clicks your result receives in the Search Engine Results Page (SERP).
These organic clicks from search visitors can noticeably affect your rankings on Google.
Here’s why:
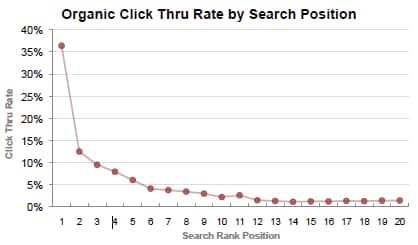
Every position on the first page of Google has an average Click-Through Rate.
Let’s suppose you are sitting at position #6 and are receiving about 4% of clicks from search visitors.
If for some reason you start receiving a higher-than-average number of clicks, Google looks at this and thinks, ‘Wow, people seem to really like this result’ and they will place it higher on the page.
On the other hand, if a search result gets less than the normal amount of clicks, Google assumes that that result isn’t a great fit for that particular keyword and will drop it further down the ranks.
What can you do to improve your Click-Through Rate?
First, we have to understand what we are optimizing.
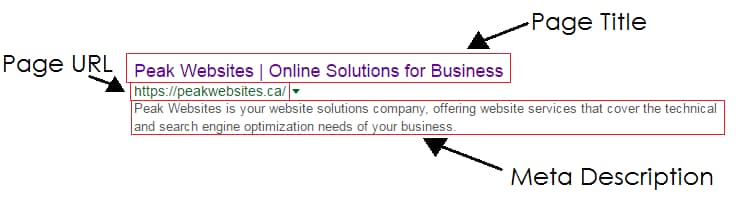
Each organic result on a Search Engine Results Page (SERP) is comprised of 3 main elements:
- The Page Title
- The URL of the page
- The Meta Description
Each element can be optimized to improve your Click Through Rate.
Here’s how:
Write Compelling Page Titles
The page title is one of the first things a user sees on the SERP, so design your page title to compel users to click on your result instead of the next guy.
There are many tips and tricks for crafting attention-grabbing headlines. Let’s take a look at a few:
Use Compelling Language
One of the easiest ways to grab attention is to use compelling language in your page title.
Carefully chosen adjectives and power words help to provoke excitement and create a sense of urgency.
Some of these words are:
- Amazing new discovery. . .
- The Secret to Losing Belly Fat
- 17 Proven Tips for Rock Solid Abs
- 99 Backed-by-Science Ways to Make Him Fall in Love With You
Another way to use language is to deal in absolutes.
For example, let’s say you’re writing a guide on how to build a Tree Fort in your backyard. Consider using words like:
- The Definitive Guide to Building A Tree Fort
- The Ultimate Guide. . .
- A Comprehensive Guide. . .
You can also speak to people’s desire for quick and easy results and add the following words to your page title:
- Build a Tree Fort Fast
- Easy steps for building a Tree Fort
- Build a Tree Fort Quickly and Easily
- Learn how to build a Tree Fort Right Now
If my page title was simply ‘How to Build a Tree Fort’ that wouldn’t be too compelling now, would it?
Effective, click-through-worthy page titles create an emotion in the reader that they can’t resist.
Here are a few examples of page titles that create an emotional response:
- How to Love the Skin You’re In
- Your Next Big Move: 5 Signs You’re Ready to Make It
- The Upside of Self-Deception
Each of these examples creates an emotion when read.
By employing emotional language in our page titles, we are much more likely to get a click from search visitors.
Here is an example from Buzzfeed, one of the best in the biz for creating highly clickable pages:
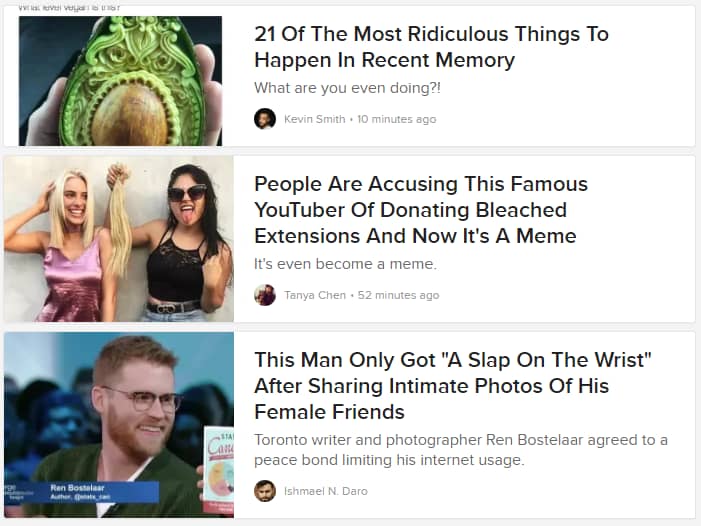
Each of these page titles creates curiosity and interest and entice visitors to click through.
The takeaway?
If you can tap into the power of emotions in your own page title, you’ll be well on your way to higher click through rates.
Include Numbers
For some reason, people love numbers. They seem to give a sense of certainty and definitiveness that can’t be beat.
As for getting higher click-throughs, page titles with numbers tend to do a better job of getting people to click on your page.
You see it all the time on magazine covers and you see it on just about every SERP.
- 11 Tips to Reduce Belly Fat.
- Save Money: 35 Ways to Cut your Expenses
- 10 Simple Ways to Flirt Better
If it makes sense for your situation, including a number in your page title will make it easier for users to want to click on your page.
Be Ultra-Specific
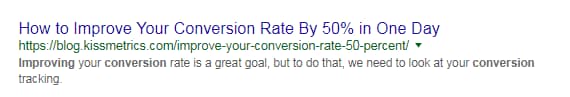
Some of the most compelling, click-through-worthy page titles I’ve seen are ultra-specific, claiming to give you a very particular result.
When I searched for improve conversions on Google, this page-title stood out:
That’s not to say the other page titles weren’t effective.
In fact, many of them employed a lot of the techniques we’ve already talked about:
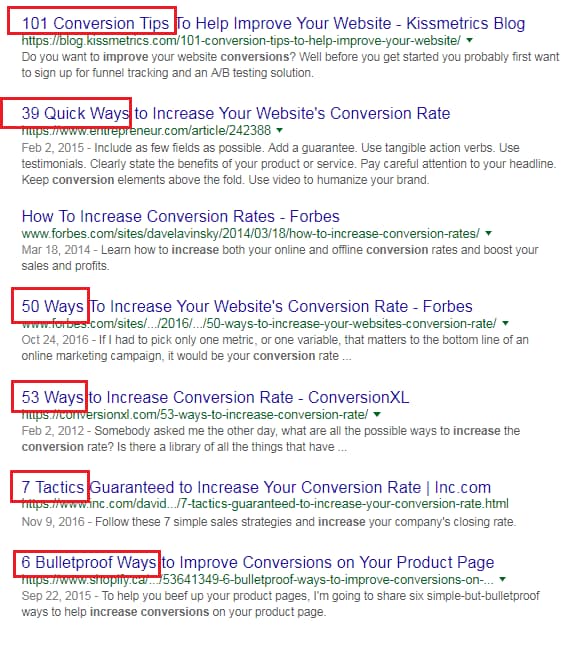
Although these many of these page titles use numbers and work to create emotional interest through compelling language, the one that caught my attention was the one that stood out!
In this case, being ultra-specific set itself apart and drew my interest.
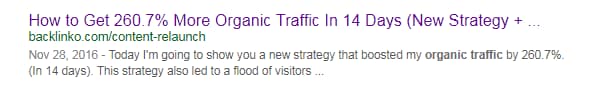
Here’s another example of a highly-specific page title:
Although this particular page title gets chopped off by Google, it is still a very compelling, super-specific page title.
It’s also no coincidence that it ranks in the top three for how to get more organic traffic, a highly competitive keyword.
Borrow from Your Competitors
Sometimes you may need a little inspiration when coming up with a winning page title so take a page from your competitors.
One of the best places to turn when you need this extra kick is the ads that appear for the keyword you are trying to target.
Think about it:
Marketers spend thousands of dollars crafting and split-testing the exact words and phrases they use to get the optimal amount of clicks from potential buyers.
You can use that to your advantage!
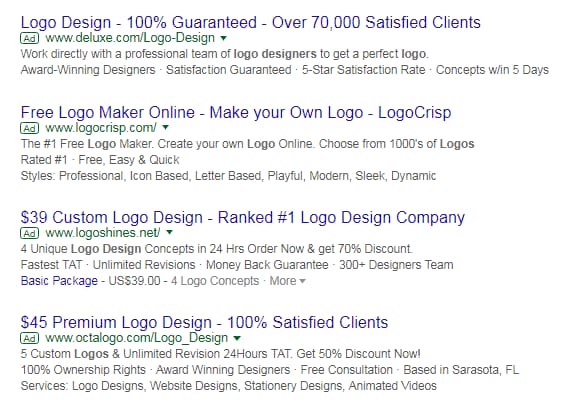
Let’s say you had a business designing logos.
Start by searching for logo design then take a look at the top ads for the keyword:
Through analyzing these ads, we can see there is emphasis placed on being #1, on having tons of satisfied clients; a couple of them even include prices (numbers) in their titles.
These techniques work – otherwise, they wouldn’t be using them!
You may even choose to mimic the format of their page titles.
For example, each title uses hyphens ( – ) to separate the different lines of text.
You can write your page title to do the same.
On the other hand, maybe you want to stand out and instead choose to implement a vertical pipe ( | ) to break up your content.
Any way you slice it, there is a lot of value to be found in analyzing paid advertisements for clues on what you can do to create more interest and entice more clicks from potential visitors.
What about including your keyword in the page title?
If you spend a little time on Google and start searching for keywords, you might notice that the words you typed don’t always appear in the page titles of the pages that are returned to you.
As we’ve already seen, Google cares less about how well you’ve optimized your page title and H1 for a particular keyword and more about how good a job your page does at providing a useful, relevant user experience to web searchers.
So don’t get too wrapped up in including your keyword in the page title.
If it makes sense to use it (or a variation of it), by all means, I would recommend it but keep in the mind the goal is to entice users to click on your page and to keep them on it by providing them with good, valuable stuff!
A few helpful tips when writing your page title:
Your page title should not exceed 60-65 characters otherwise it risks being truncated by Google.
Incidentally, this is also the case on mobile phones.
It’s also a good practice to place your keywords closer to the beginning of your page title, as this immediately tells users what they’re looking at (and avoids critical words in your page title from being cut off).
You can verify your page title by viewing the source code of the web page.
To view the source code for a particular web page, right-click somewhere on the page and select view page source.
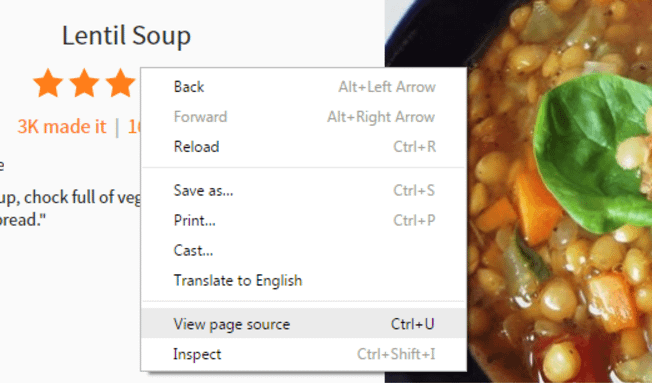
From there, look for the <title> tag.
You can quickly locate the title tag by employing the find feature (pressing ctrl + F) and then typing in <title.
At the end of this section, I will show you a few valuable online tools you can use to test out how your page title, page URL, and meta description will appear on Google, so keep reading!
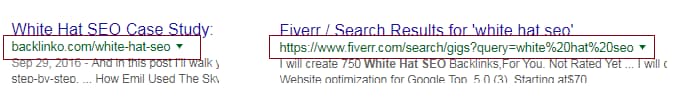
Have a Clear Page URL
Page URLs get the least attention from unsuspecting visitors and on SERPs but this doesn’t mean that they should be ignored!
In fact, the URL of your page can sometimes be the final push a user needs to decide to click on your page and not a competitor’s.
Which page URL looks better to you:
I don’t know about you but if I was discerning, I’d click on the clean, pretty one.
Now, this might be a bit of an exaggeration as less and less you’ll find page URLs like the second one ranking on the first page of Google but it’s something to be aware of.
Although the URL of your page won’t make or break your rankings, strive to make your page URLs as short and concise as possible.
As an added SEO tip, including your target keyword in the URL will go a long way in scoring you additional ranking points over your competitors.
The Final Piece: The Meta Description
Much the same as the page title, the meta description is a secondary area of text that provides another opportunity to entice someone to click on your page.
It should not exceed 165-175 characters in length and, much like the page title, should include compelling language that summarizes the content on the page and draws people in to want to learn more.
It’s a good idea to use keywords or related terms in your meta description, although they don’t contribute to higher rankings.
They do, however, appear bolded, and this provides additional relevancy signals to searchers when they’re trying to decide which result to click on.
If you can show in your meta description that your page content deals with the very problem the searcher is looking to solve then you’re far more likely to get a click and, with that, watch your ranking climb higher up the SERPs.
But be warned, Google doesn’t always use your meta description in its results.
Sometimes Google will grab an excerpt of content from your page if it feels like that content better conveys the meaning of your page.
Regardless of how Google displays your result in the SERPs, you should always write a meta description because it gives you one more way to improve your clickablity and optimize your web content for search engines.
Plus, you never know when Google might switch around what it chooses to show its users so go the extra mile and write a clear, descriptive and compelling meta description.
Search Results Testing Tools
As promised, here a few tools to preview how your page title, URL, and meta description will look in Google:
These tools also offer the option to preview your snippet with additional SERP features like Rich Snippets, bolded text and dates.
Although all these tools do a good job of replicating Google SERPs, they are only approximations of the real thing.
Ultimately, the best place to view your optimization strategies at work is from Google itself so once your page is live, search for your keyword on Google and see how your page looks in the SERPs in real-time.
Click-Through Rate: What it All Boils Down To
At the end of the day, there are dozens of formats and strategies you can use to write compelling, click-worthy page titles but what it all boils down to is how well you grab people’s attention and sell them on the benefits they will get from clicking on your page.
If you can convince search visitors that you have the answer to their problem through an interesting page title, a clean URL, and compelling meta description, you are in a strong position do well on the SERPs.
And of course, having a way to monitor your CTRs can be helpful, too, so that you can find out which page titles are working and which aren’t.
5. Increase Dwell-Time
Though its significance is often debated, dwell time, or the amount of time a reader spends on a page is regularly considered a strong signal to Google that a web page deserves to rank higher in the SERPs.
So just how do we keep visitors on our page and improve our dwell time?
Make Relevant Content
Part of what keeps a reader glued to your page is the degree of relevancy that your content provides.
In other words, how well does your content match the searcher’s intent?
If the content doesn’t match the intent of the searcher, then page visitors will click the “back” button and you’ll eventually drop down the rankings for the keyword they used to find you.
So how do you make your content more relevant?
Understanding your audience and what they want is the first step.

The more you understand what your audience wants, the better you can deliver relevant information to them.
The other piece to having relevant content is doing your keyword research and uncovering the intent behind the keywords that receive the most monthly searches.
For example, someone who searches for best cell phones 2017 is researching what phone to buy. On the other hand, someone typing in Samsung s7 unlocked 16gb knows exactly what phone they want.
The intent of both of these keywords is completely different.
Getting into the heads of those who are typing in your keywords and then crafting content that is relevant to that intent is one of the best ways to keep people sticky to your page and increase dwell time.
Website Usability
Not to be confused with User Experience, the usability of a website is the ease in which a site visitor can perform their desired task.

As you can probably imagine, a website that isn’t usable doesn’t fare very well on Google and leads to lower user engagement, fewer conversions, and ineffective SEO.
Here are some of the things you should focus on to optimize the usability of your website:
- Ease of Navigation – Is your navigation easy to follow and easy to use? Can people find what they’re looking for?
- Font Size – There’s nothing worse than itty-bitty text that you can’t read. Unless you know how to zoom in in the browser, you’re in for a tough read and probably aren’t going to stick around.
- Use of Headings – Headings and sub-headings separate content into logical segments and make scanning through a web page to find information a breeze.
- A Clean Design – There’s nothing worse than a noisy page littered with ads and annoying pop-ups so reduce the clutter and aim for a design that puts your content front and center.
Employ Multimedia
Using multimedia like images and videos on your blog or web page is a proven way of increasing user engagement and dwell time.
Additionally, web pages with images tend to garner more social shares.
Just be sure that you optimize your multimedia content properly to get the biggest SEO bang for your buck.
To start, apply good naming conventions to your multimedia files by using hyphens ( – ) to separate words.
Hyphens are the preferred format when it comes to search crawlers indexing your multimedia.
It’s also a good idea to use short, descriptive filenames as images get indexed by Google and may appear in Google image search – another way to drive traffic to your website.
So instead of something meaningless like:
015675567.jpg
be clear and descriptive and write:
girl-sits-at-desk.jpg
If you’re using an image that adds context to your blog page, make sure to write alternative text.
Alt text, as it’s more commonly known, describes the content of an image for those with certain disabilities who may not be able to see the image on the screen.
Alt text also has the added benefit of adding more relevant context and information to your content that Google can better use to rank and index your material.
Alt text is not always necessary, for instance, when you use an image that is purely decorative and adds nothing to the meaning of the page. In this case, it’s customary to leave the alt text blank.
A good guide for when to use alt text can be found here.
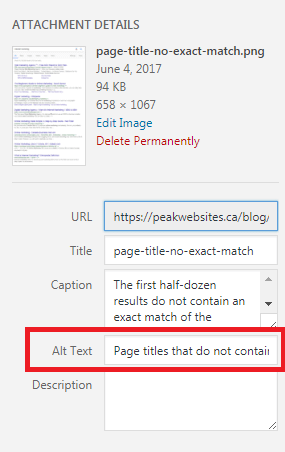
You may already be used to including alternative text with your images. If not, here’s how to do it in WordPress easily:
When you upload or access an image from the Media menu, you have the option to fill in the alt text.
If you’re not using WordPress, simply add the alt attribute to the img tag in your code editor:
<img src="/" alt="describe your image here" />
If using other multimedia such as videos or infographics, it’s a good idea to include a text transcription. This not only makes your content more accessible to people with disabilities but provides easy-to-crawl content for web crawlers to consume.
Any type of multimedia that employ helps break up the monotony of text and gives the reader a break. Employing different types of elements also gives you more ways to implement your various keywords, diversifying how keywords are included on the page.
Internal Links
Internal links – linking from one page of your site to another page within your website – are great for a number of reasons:
For starters, they provide extra SEO juice to the pages you link to, improving the page rank of those pages.
They also improve the usability and user experience of your website by linking to other relevant content, increasing the amount of time someone stays on your site.
This is a total win-win.
Not only that, internal links help to tell Google what pages of your site should be crawled.
As Google is limited to the number of sites and pages they can crawl, they allot what’s called a crawl budget to each website it scans.
Once your website has run out of crawl time, they crawler leaves and moves onto another site.
When you link to another page or article within your website, you are essentially helping to tell Google what pages on your site it should crawl and index.
This helps to provide increased exposure for that particular page and improves its visibility on Google.
If you write content around a particular niche or provide products and services that you talk about in your writing, keep an eye out for logical, natural places in your writing to link internally.
Make the link text descriptive and avoid meaningless phrases like click here as they add no context to readers or search crawlers.
Conclusion
Google is not the search engine it used to be.
In order to rank better in 2017, we have to play by Google’s rules and that means creating content that is useful and accessible to its users.
The more and better able we are to do that, by focusing on accessibility issues like speed and mobile-readiness, creating useful content that is relevant and solves a searcher’s intent, the more we will be supported in the SERPs.
There is much more that could be said on the topic – in fact, the sections above only scratch the surface of improving your Google rankings!
If there are any particular areas that you would like to learn more about, please let me know by leaving a comment below or contacting me directly.
I would love to dive deeper into any one of these subjects, especially if I know there is a curiosity for them.
Thanks for reading and good luck in the SERPs!